Debug layer connections
Input and output shapes
The simplest way to debug network is just to explore input and output shapes. Basic information about network’s input and output shapes can be seen when network printed.
>>> from neupy.layers import *
>>> network = Input(10) >> Relu(5) >> Softmax(3)
>>> network
(?, 10) -> [... 3 layers ...] -> (?, 3)
In addition, network has two attributes that can provide with direct access to the information about input and output shapes.
>>> network.input_shape
TensorShape([Dimension(None), Dimension(10)])
>>> network.output_shape
TensorShape([Dimension(None), Dimension(3)])
Notice that output shapes in the network specified using TensorShape class from Tensorflow library.
Visualize networks
Information about input and output shapes from each layer can be visualized with show method.
from neupy.layers import *
network = join(
Input((10, 10, 3)),
parallel([
Convolution((3, 3, 32)) >> Relu(),
MaxPooling((2, 2)),
], [
Convolution((7, 7, 16)) >> Relu(),
]),
Concatenate(),
Reshape(),
Softmax(10),
)
network.show()
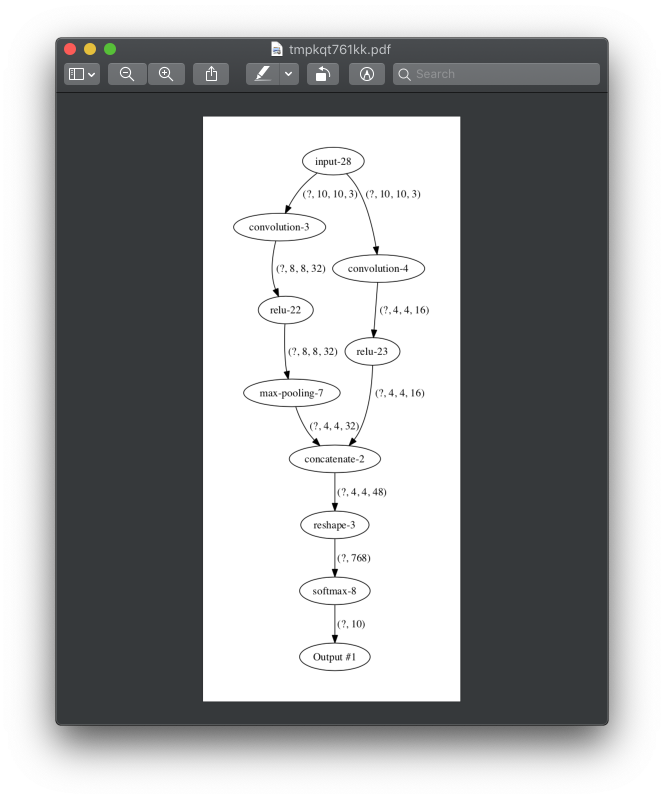
This function will pop-up PDF file with a graph that defines all layers and relations between them. In addition, it shows input and output shape per each layer.
Count number of parameters
The n_parameters attribute returns number of parameters in the network
>>> from neupy.layers import *
>>>
>>> network = join(
... Input(10),
... Relu(5), # weight: 10 * 5, bias: 5, total: 55
... Relu(2), # weight: 5 * 2, bias: 2, total: 12
... )
>>> network.n_parameters
67
Iterate through all network parameters
Networks variables can be accessed from the variables attribute.
>>> network = Input(1) >> Sigmoid(2) >> Sigmoid(3)
>>> network
(?, 1) -> [... 3 layers ...] -> (?, 3)
>>>
>>> for (layer, varname), variable in network.variables.items():
... print("Layer: {}".format(layer.name))
... print("Name: {}".format(varname))
... print("Variable: {}".format(variable))
... print()
...
Layer: sigmoid-1
Name: weight
Variable: <tf.Variable 'layer/sigmoid-1/weight:0' shape=(1, 2) dtype=float32_ref>
Layer: sigmoid-1
Name: bias
Variable: <tf.Variable 'layer/sigmoid-1/bias:0' shape=(2,) dtype=float32_ref>
Layer: sigmoid-2
Name: weight
Variable: <tf.Variable 'layer/sigmoid-2/weight:0' shape=(2, 3) dtype=float32_ref>
Layer: sigmoid-2
Name: bias
Variable: <tf.Variable 'layer/sigmoid-2/bias:0' shape=(3,) dtype=float32_ref>
In case if variables in the network don’t have defined parameters, the variables method will go through the layers in the network and trigger create_variables method per each layer.